This is a Scedosporium. Let us tell you more about it.
Definition
Scedosporium is a ubiquitous filamentous fungus present in soil, sewage, and polluted waters. It causes a wide variety of infections. The most frequent infection is through the respiratory tract, but localized infection can become invasive and extend to surrounding tissues or through the bloodstream.
Invasive scedosporiosis can represent up to 1/3 of the fungus infections due to non-Aspergillus molds, depending on geographical localization and underlying disease.
Infections symptoms
Scedosporiosis clinical presentations are pulmonary and cerebral diseases, localized skin or soft tissue infection, and joint and bone diseases. Fungal infection mainly occurs in immunocompromised patients (with hematological malignancies, after solid organ transplantation) but it has also been reported in the immunocompetent usually occurring after trauma: near drowning or inoculation.
Diagnosis
Despite the lack of approved biomarker tests, early diagnosis is critical to patient survival. The detection is reliant on the culture of pathogens from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, tissue biopsy, or blood.
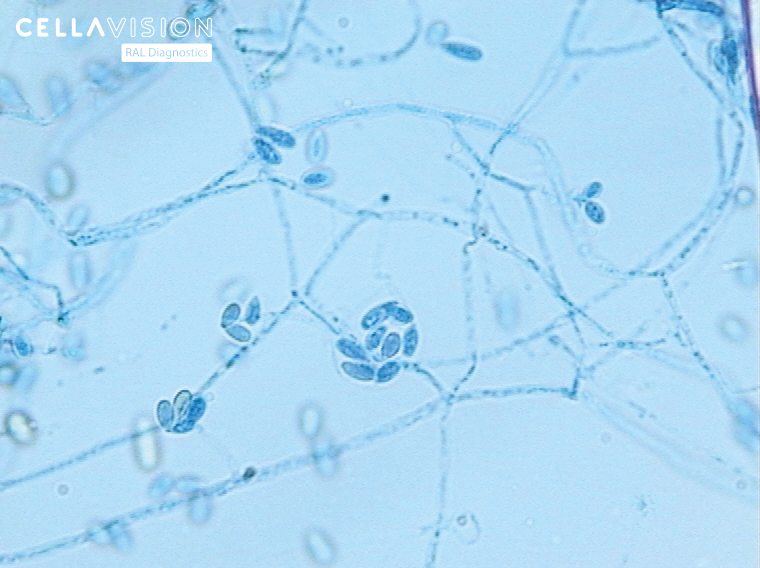
Several diagnostic techniques can be applied to Scedosporium infections according to the type of infection: microbiology (direct staining and culture), histopathology, radiology, and serological and molecular biology. Microbiology involves staining with, for example lactophenol blue as can be seen in the quiz photo.
The treatment of Scedosporium infection is challenging because of its resistance to anti-fungal agents. An early and accurate diagnosis is essential to provide appropriate treatment. These fungi may be confused histologically with Aspergillus spp. and other hyalohyphomycetes with differing antifungal resistance.
See you next month for another Quiz 🎲!