Monthly Cell Challenge #1 / 2024
Child with reactive and necrotic lymphocytes on peripheral blood film
Description:
4-year-old girl with fever, stuffy nose, inflamed tonsils with white spots, and swollen lymph nodes was seen by her pediatrician. A Monospot test was negative.
Blood was sent for CBC:
| Test | Result | Units |
|---|---|---|
| WBC | 4.5 | x109/L |
| HGB | 13.3 | g/dL |
| MCV | 82 | fL |
| PLT | 185 | x109/L |
Atypical Lympho? flag triggered blood smear analysis on Cellavision DC-1
| WBC Differential | % | x109/L |
|---|---|---|
| Neutrophils | 30 | 1.35 |
| Lymphocytes | 40 | 1.8 |
| Variant (Reactive) Lymphocytes | 26 | 1.17 |
| Monocytes | 3 | 0.14 |
| Eosinophils | 1 | 0.05 |
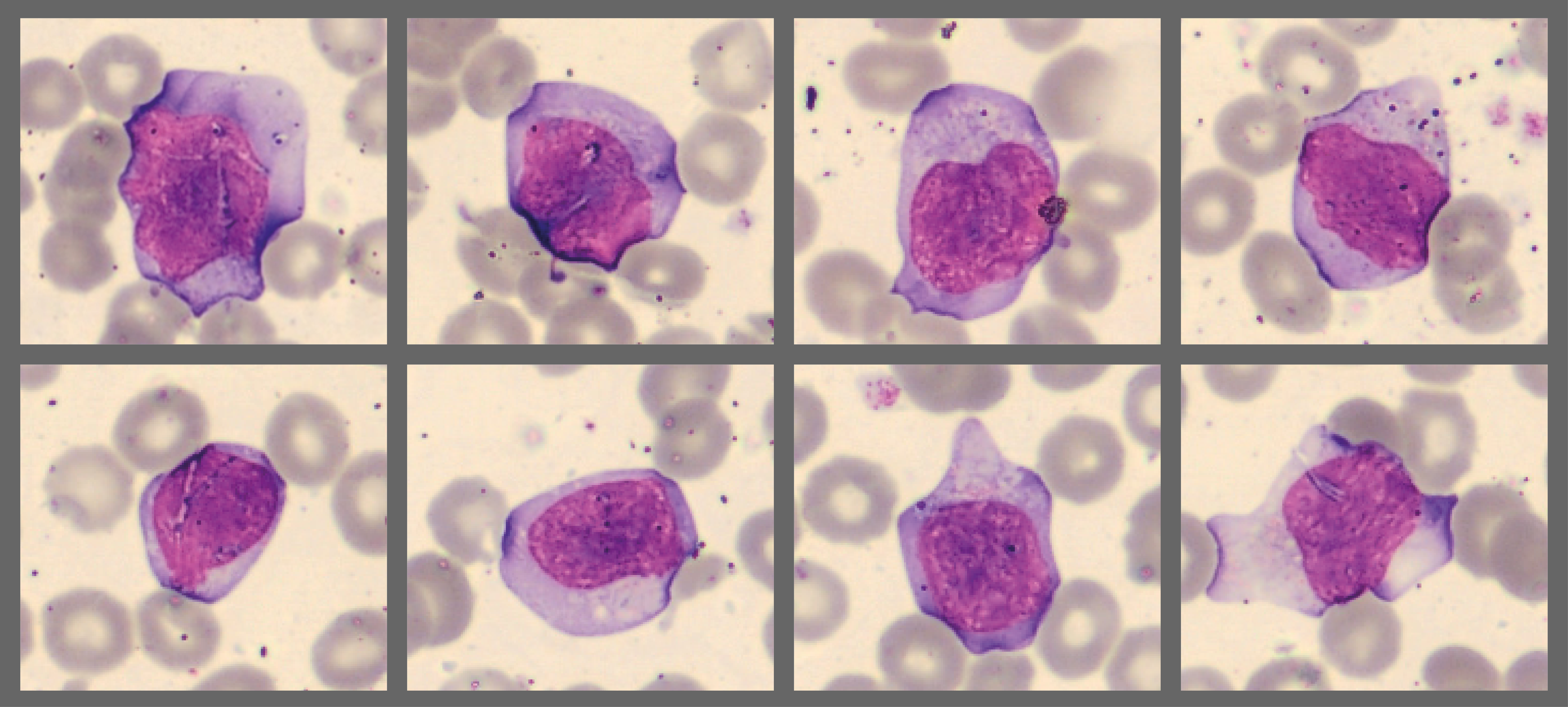
Reactive lymphocyte:
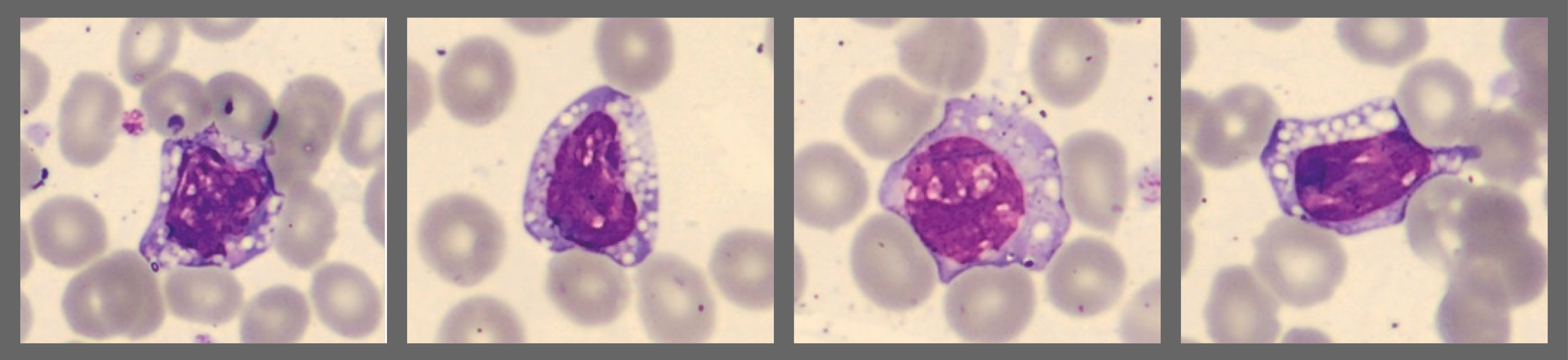
Some of the lymphocytes appeared apoptotic (necrotic/degenerated) with cytoplasmic vacuolation:
Diagnosis
Infectious mononucleosis (IM)
Despite a negative monospot test, the pediatrician remained suspicious of infectious mononucleosis (IM). As a result, Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) testing was performed. The results were positive, confirming a diagnosis of IM.
IM is caused by acute infection with EBV. The Monospot heterophile test is falsely negative in 40% of children (< 5y) with IM.1 As a result The CDC does not recommend general use of the monospot test.2 EBV antigen and antibody testing has better sensitivity/specificity and should be done in heterophile negative patients with a high degree of clinical suspicion – as in this case.
Apoptotic lymphocytes can be found in blood films of up to 90% of IM cases.3 In this patient, both apoptotic and reactive lymphocytes were clearly visible with Cellavision which provided additional clues in the diagnostic workup of IM.
___
1. Marionneaux SM. Nonmalignant leukocyte dirorders. In: Keohane EM, ed. Rodak's Hematology. 7th ed. Elsevier; 2024:chap 26.
2. CDC. Laboratory Testing for Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. August 27, 2024. Accessed August 27, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/epstein-barr/php/laboratories/index.html
3. Fisher MS, Jr., Guerra CG, Hickman JR, et al. Peripheral blood lymphocyte apoptosis: a clue to the diagnosis of acute infectious mononucleosis. Archives of pathology & laboratory medicine. Oct 1996;120(10):951-5.