Burkitt Lymphoma
Description
A 9-year-old male with a history of jaw pain and weakness presented in the emergency room with fever, shortness of breath, and severe abdominal pain.
| Test | Results | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| WBC | 16 | x109/L |
| HGB | 9 | g/dL |
| MCV | 88.1 | fL |
| PLT | 56 | x109/L |
The CBC results were flagged with Blasts/Abn Lympho which triggered analysis on Cellavision DC-1.
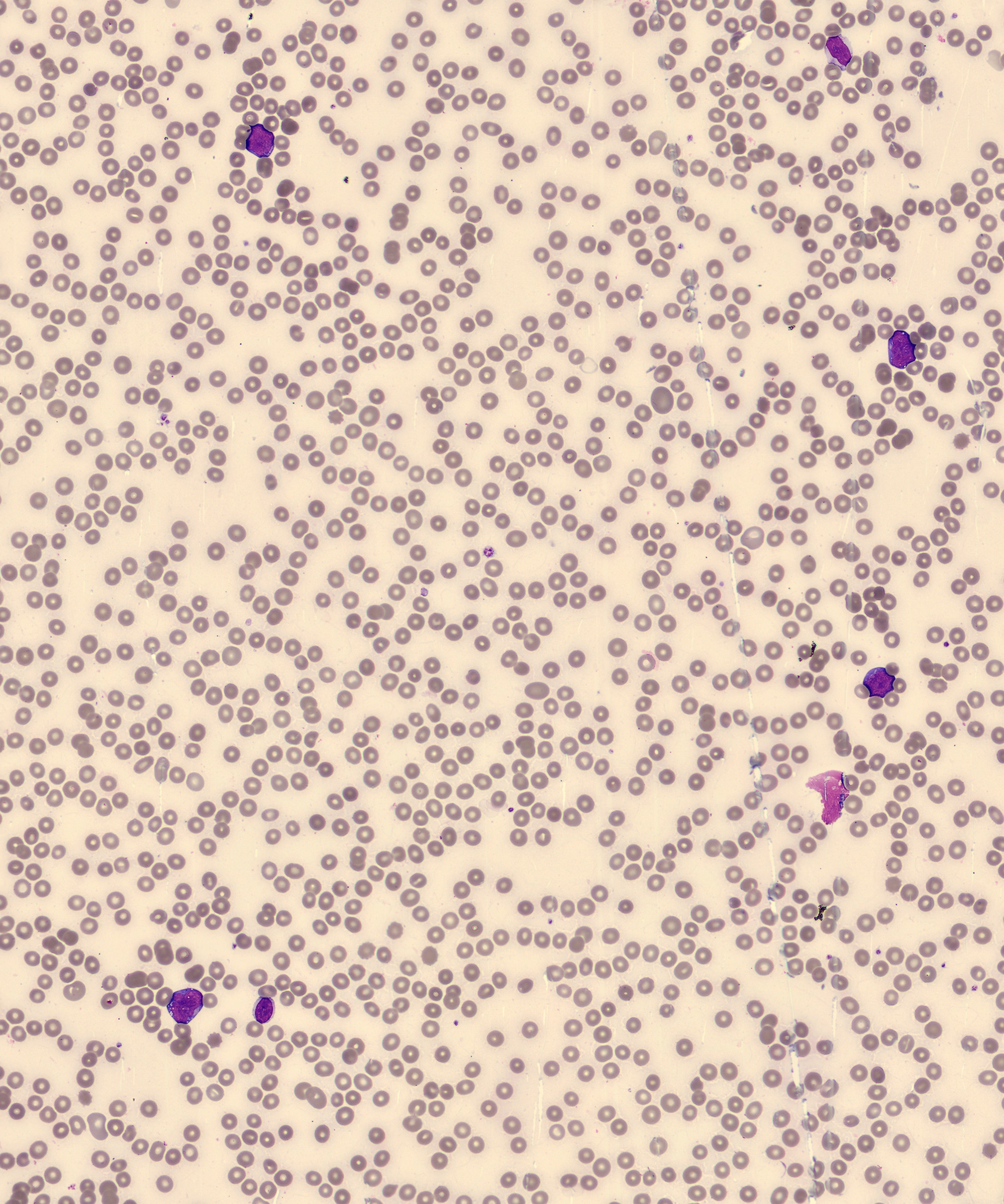
Cellavision differential found 65% numerous med-large immature cells with high N:C ratio, fine chromatin, nucleoli, and deeply basophilic cytoplasm with distinct vacuoles in most cells. They were reported as blasts (see below).
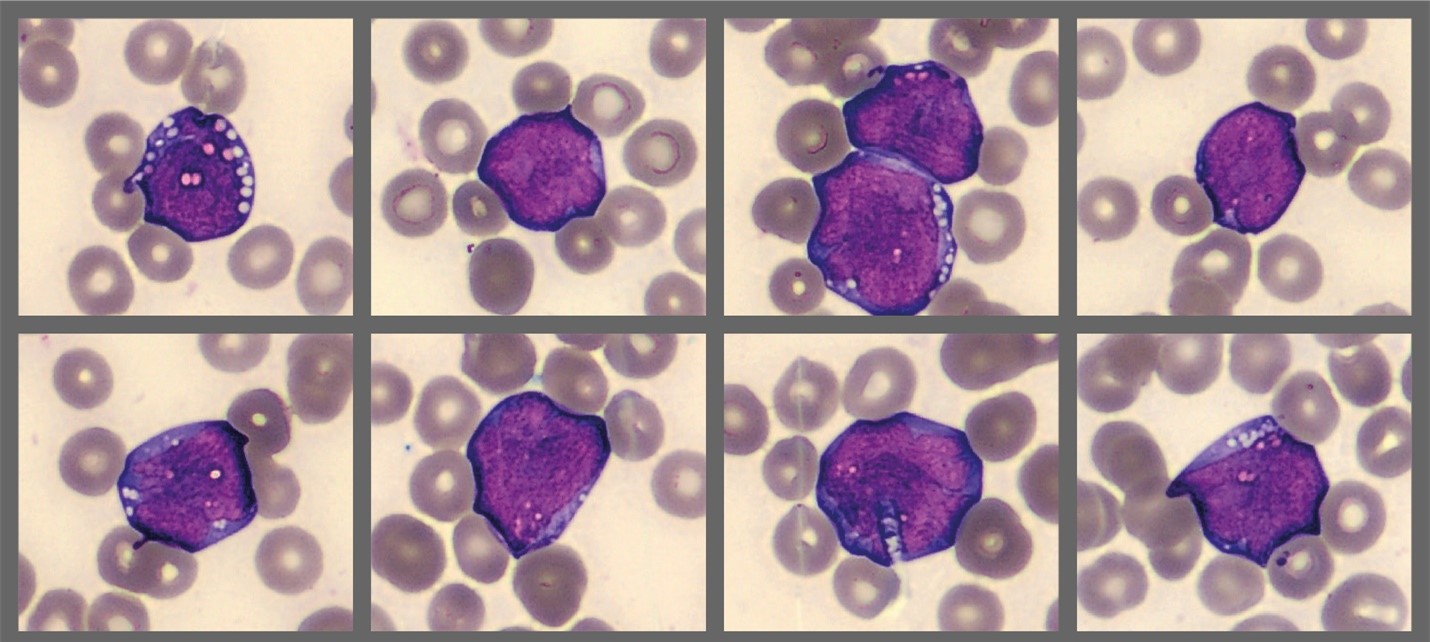
Diagnosis/Summary
Blood and bone marrow samples were evaluated. Results:
- Flow cytometry: the abnormal cell immunophenotype: CD10+, CD19+, CD20+, CD22+ CD43+, CD79a+, BCL6+, CD23-, CD5-, BCL2 -,TdT-
- Immunohistochemistry: Ki-67 positive in 100% of cells
- Karyotyping identified t(8;14)
These findings confirmed the diagnosis of Burkitt lymphoma
Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is a highly aggressive, rapidly growing B cell malignancy. When diagnosed, most patients already have metastatic disease. Many EBV patients are chronically infected with EBV.
In 80% of BL cases, a chromosomal translocation, t(8;14), creates a fusion between the c-MYC gene and IGH gene. c-MYC normally controls cell cycling and is tightly controlled. The gene fusion leads to continuous activation of c-MYC, and accelerated mitosis of malignant cells.
There are 3 forms of BL: endemic, nonendemic (sporadic), and immunodeficiency related. Endemic BL is the most common childhood cancer in Africa where jaw and facial bone tumors are frequent. Nonendemic BL is seen in children and young adults in the Western world. Immunodeficiency subtype mostly occurs in AIDS patients. The endemic and nonendemic classifications are defined mostly by geography and epidemiology.1 There are no defining molecular differences to separate the two subtypes. In 2024, the WHO suggested a future classification of BL based on EBV status: EBV neg BL and EBV pos BL, because they differ in underlying cell biology and genetic pathology.1
BL tumors can affect numerous sites in the body – but not often in bone marrow and blood, except in the Western world where smear reviews detect BL cells in up to 30% of patients.2
Reporting BL cells in the differential
The ICSH recommends counting BL cells as lymphoma cells in the WBC differential.3 However, in order to comply, the lab scientist should have access to diagnostic information during testing4. Without it, BL cells may be misclassified. For example, besides shared blast characteristics, vacuoles and dark blue cytoplasm in BL cells can sometimes be found in myeloblasts and other cells. The morphologic characteristics of BL cells are not necessarily unique. A quick check of the diagnosis would help ensure accuracy and precision in differential results and support accurate clinical assessments.
If BL cells are classified as blasts, a comment about their morphology (i.e. dark blue cytoplasm with vacuoles) could be helpful to the clinician, especially in 1st time patients. Regardless of how BL cells are classified (lymphoma cells or blasts or something else), consistency in cell classifications on an individual patient in day to day and tech to tech testing is essential.
___
1. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Haematolymphoid tumours [Internet]. 5th ed. International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2024.
2. Blum KA, Lozanski G, Byrd JC. Adult Burkitt leukemia and lymphoma. Blood. Nov 15 2004;104(10):3009-20.
3. Palmer L, Briggs C, McFadden S, et al. ICSH recommendations for the standardization of nomenclature and grading of peripheral blood cell morphological features. Int J Lab Hematol. Jun 2015;37(3):287-303. doi:10.1111/ijlh.12327
4. van der Meer W, van Gelder W, de Keijzer R, Willems H. The divergent morphological classification of variant lymphocytes in blood smears. J Clin Pathol. Jul 2007;60(7):838-9. doi:10.1136/jcp.2005.033787